Peer-To-Peer Crypto Trading NZ NZ Crypto Guide
Looking to maximize your freedom and privacy and take your crypto endeavors to another level? P2P may well be the method for you.
Disclaimer
This guide is provided for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial or investment advice. The information contained in this guide is based on publicly available sources and our own experience, and we make no representations of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, security, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the information provided. As an individual, you are solely responsible for conducting your trades and engaging with other members of the community. We recommend taking extreme caution and care when trading and are not responsible for the outcomes, management, or oversight of your activities. We do not vouch for the authenticity of any trader, and it is exclusively your own responsibility to perform due diligence when trading. Please note that cryptocurrency trading carries significant risks, and you should only move funds that you can afford to lose.

As more and more Kiwis become aware of how their personal and financial activities are being tracked and recorded, the idea of trading crypto peer-to-peer (P2P) is becoming increasingly appealing. But how exactly can you buy or sell crypto using peer-to-peer?
I’m Harry Satoshi, the creator of the NZ P2P Crypto Marketplace, and this is my no bullshit guide on P2P crypto trading in NZ – how you can secure your privacy with peer-to-peer.
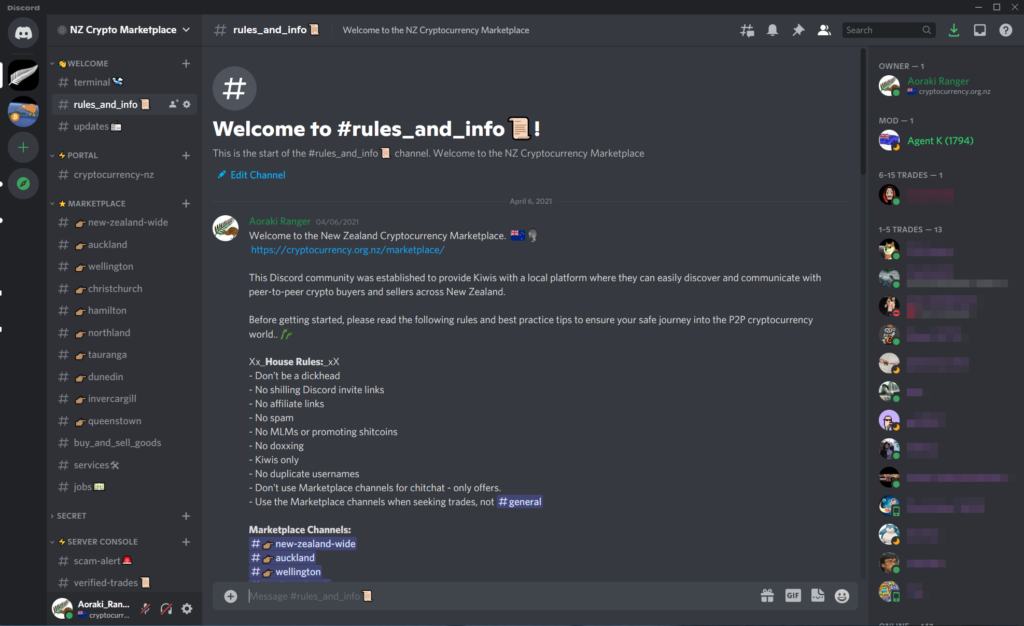 Go To NZ P2P Marketplace
Go To NZ P2P Marketplace⚠️Scam warning: This is for experienced NZ crypto users only!⚠️
What is Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Crypto Trading?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) crypto trading is the act of buying or selling crypto like Bitcoin directly between two individuals, (one seller / one buyer), without the use of a middleman (like a KYC'ed exchange, more on that below) to facilitate the transaction process and execution.
P2P is one of the the most private ways to acquire crypto in the world, negating the use of a middleman or central authority, who are often required by law to track your activity. You have the freedom to voluntarily enter P2P trades with whoever you deem trustworthy, like buying or selling an item from users on Facebook Marketplace.
You can choose whether or not you want to provide your ID, whereas on regulated crypto exchanges and retailers, KYC / providing your personal info is mandatory. The two individuals (peers) can decide on their own price, terms, process and action plan to execute the transaction. Both traders are solely responsible for it's execution.
P2P comes with a much higher risk as there are many scams and scammers in the P2P world, but successful trades offer unparalleled privacy for acquiring digital assets in NZ. So with that all said, why do New Zealanders choose to P2P (or person-to-person) in NZ?

P2P Crypto Trading Pros & Cons
Trading Bitcoin, Ethereum, Monero or other crypto P2P comes with it's own unique pros and cons, providing contrast as to how easy it is to accumulate crypto in NZ via KYC.
Pros
- Decentralised: P2P trading is decentralized, meaning that transactions occur directly between buyers and sellers without the need for intermediaries like banks.
- Privacy: P2P trading can offer greater privacy compared to centralized exchanges since users are not required to provide extensive KYC information.
- More options: P2P trading can offer more payment options, including cash or bank transfers, or swapping other assets, reducing limits for what constitutes crypto trading.
- Lower Fees: P2P can have lower fees compared to centralized exchanges, as there are no middlemen to charge fees for transactions. However you will often encounter traders selling at a markup.
- Accessibility P2P trading can be more accessible to users in regions where centralized exchanges may not be available due to regulatory or infrastructure issues.
Cons
- Risk of scams: P2P trading poses serious risk of scams, as users may be vulnerable to fraudsters who misrepresent themselves or their offers.
- Limited liquidity: P2P trading may have limited liquidity compared to a cex, meaning that it can be more difficult to find buyers or sellers for certain crypto or at certain prices.
- No order book: P2P trading does not have an order book, which can make it more difficult for users to determine market prices.
- Limited dispute resolution: P2P trading has near zero dispute resolution options compared to centralized exchanges, which have more resources and procedures for handling disputes.
- Security risks: P2P trading can pose security risks to users if they do not take proper precautions to protect their private keys and personal information.
- 5 dollar wrench attacks: if you meet up to execute P2P trades in the flesh, this can pose serious danger. Read more.
The World of P2P Crypto Scams & Scamming
From what I've witnessed with my own eyes, the P2P trading world is completely infested with scammers, imposters and shitheads who you will need to watch out carefully for. It sounds brutal but basically, you shouldn't P2P unless you have an extremely high tuned bullshit radar and you're in a position where you can lose your money and learn a lesson.
Essentially, instead of relying on regulated services and their proven credibility and legal accountability, you're instead relying on the reputation and good faith of a particular trader, to carry out and execute the trade on the terms you both set. There are platforms that offer P2P escrow services, however this guide is based around raw, no middleman trades.
Below is a list of the most common P2P scams. They vary in style and savviness, but understanding how they operate may save you from becoming another scam statistic.
Impersonation scams: where scammers pose as trusted entities such as reputable traders, admins, a friend, a business owner, celebrity or well known personality, to gain your trust and convince you to send your Bitcoin – for the scammer to exit once sent.
Payment reversal: where scammers initiate a trade with a reversible payment method such as PayPal, credit card or bank transfer. Once they receive the Bitcoin, they reverse the payment, leaving the seller without either the Bitcoin or the payment. All too common.
Phishing: when scammers create fake websites or emails that look like legitimate P2P platforms, to trick you into clicking dodgy links which can reveal your login credentials, private keys or other personal information. Never click on links you don't know or trust. You should never have to click any links or sign up to anything when executing P2P trades.
Fake escrow service: where scammers ask a 'friend' or a sock puppet account to 'hold the Bitcoin safely in the middle' to be released when the trade is complete. They're in control of both the accounts, and once they receive your Bitcoin (BTC), they block you and vanish.
Fake wallet scams: when scammers convince an aspiring P2P user to use a particular wallet that is backdoored, so the scammer can just empty the users 'wallet' and vanish.
Social Engineering: broadly used in almost all P2P crypto scams. If you don't know this word, research it. Basically when scammers create fabricated testimony, affirmation or feedback via all kinds of tricks, to establish trust and rapour to convince you to send.
As admin of the NZ P2P Crypto Marketplace, my username (Aoraki_RangerNZ), profile picture and account bio is frequently mimicked by imposter scammers to leverage my authority as a known member. New entrants to the server receive messages from these imposters, pretending admin is 'looking to trade'. This is what I mean by a bullshit radar.

P2P Trading tips & Best Practices
They may sound extreme but following them is your most sure way to not get scammed.
Always verify the real life identity of your trader, essentially performing your own KYC due diligence background check. If they don't feel comfortable with this, there are other traders who are willing to do so. It ensures you can follow up if the trade goes sour.
Always assume by default your P2P counterpart is a scammer, unless proven otherwise. Assume 2/3 'hey want to P2P trade' messages you receive will be scams.
Use secure payment methods that can not be reversed, i.e. cash or crypto.
It's very easy for scammers to photoshop / fabricate a 'payment sent' screenshot, or a bank statement. Even if it arrives in your account, it can still be reversed. Bank payment reversal post-trade a very common scam method in the NZ P2P scam game.
Use a Kiwi based P2P trader, always assume overseas 'NZ' P2P traders are scammers.
Meet your seller in the flesh, either on trade day or beforehand, in a public place like a library or outside a police station. P2P is legal, do it in the day time at a secure location.
Always read the rules of P2P groups / platforms to prevent getting an unnecessary ban.
If you're given any reason to be suspicious, use your intuition and find another trader.
Explore the P2P platform you are using, see who's making confirmed trades. Ask for vouches from other members. Remember that an anonymous 'good' trader can suddenly go bad if presented with an exit opportunity, forgoing reputation for money.
Converse with other P2P traders in NZ to learn from their experiences and lessons.
Keep a record of your trades for reasons such as tax documentation. P2P traders are still expected to fulfil tax obligations and so forth. NZ Crypto Tax Guide coming soon.
It's not a bad idea to test a potential P2P buyer or seller with $100, without overstating you want to purchase more. This will allow you to scam test a prospect trader, but also keep in mind scammers are willing to wait months before they close their trap and bail.
Locating a P2P Buyer/Seller in NZ
You can find P2P buyers and sellers cross New Zealand fairly easily, such as on the NZ P2P Crypto Marketplace, Facebook, Reddit, Discord, forums, family and via friends etc.
As per the #rules on the NZ Crypto Marketplace, admin's don't vouch for the reputation, legitimacy or authenticity of any trader, so I can't provide any suggestions from here.
However after a bit of exploring and lessons learned, you may find your step. I hope this Cryptocurrency NZ guide has provided you value in one way or another, there's a bucket load more information and lessons infused into the text channels on our Discord.
NZ Crypto Marketplace Disclaimer: As an individual, you are entirely responsible for how you conduct your trades and engage with other members of the community. NZ Crypto Marketplace admins recommend taking extreme caution and care when trading and are not responsible for the outcomes, management, or oversight of your activities. We do not vouch for the authenticity of any trader, and it is exclusively your own responsibility to perform due diligence when trading. This is the challenge of P2P – if you cannot operate safely on your own, you may be better suited to traditional methods of buying and selling crypto. See our guide for how to buy cryptocurrency in NZ here.
P2P Keyword Glossary
Fiat Currency: government issued currencies like the NZD, USD, AUD and so forth.
Cryptocurrency: decentralized digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum and Monero.
(VASP) Virtual Asset Service Provider: crypto exchanges or service providers that fall under a specified category whereby they are required to comply with NZ AML / KYC laws.
(KYC) Know your Customer: essentially an ID verification user wall that requires you to verify your identification so you are able to buy and sell cryptocurrency through a VASP.
AML Anti-Money-Laundering: a set of laws, regulations, and procedures aimed at preventing and detecting money laundering and terrorist financing activities in NZ.
Crypto On/Off Ramps: an exchange service like Easy Crypto or Binance that facilitates a role in the process of converting fiat currency into cryptocurrency, and visa / versa.
So Why Do Kiwis P2P in the First Place?
Following the inception of the Bitcoin revolution, igniting back in 2008 when Satoshi Nakamoto released his whitepaper 'Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System'; governments, unelected transnational conglomerates and both global and local financial watchdogs have been monitoring the emerging crypto market in aims to better understand the world's shifting financial power dynamics – and the threats posed to the existing financial matrix by Bitcoin and other private decentralized cryptocurrency, like Monero.
Following the conclusion that governments can't effectively ban or censor Bitcoin directly, despite multiple high profile calls for it, regulators have instead pursued another strategy of control whereby all regulated fiat-to-crypto on and off ramp services must follow particular rules, at the expense of the individual's privacy and in the favour of the surveillance state.
Rules including reporting all KYC information to the NZ Government and IRD on request.
In response to this, many New Zealanders have chosen to obtain cryptocurrency via P2P, to negate the requirement to provide their personal information, which by doing so leads to increased capabilities of authorities or private entities to monitor your financial activity.
New Zealanders P2P for all sorts of reasons, with the intent being to maximize privacy.
Note: you can still exchange your personal information before or during a P2P trade.
What is KYC - Know Your Customer?
KYC stands for "Know Your Customer", and it's a process and requirement that regulated financial institutions and businesses must use to verify the identity of their customers, whether here in NZ or abroad. KYC assesses the potential risk of a user engaging in illegal activity such as fraud, money laundering, terrorist financing, and to prevent theft / ID fraud.
KYC is required by most financial services, including banks or 'Virtual Asset Service Providers", and involves the collection and verification of personal information including your:
Legal name.
Date of birth.
Address.
Contact details.
Identification documents.
Source of funds proof.
Note: KYC legislation is all publicly accessible information.
However KYC data collection often goes beyond this, especially once a person has engaged with trading activity on a KYC'ed platform, examples being:
IP address and device fingerprints used for access. Login history and activity logs, including timestamps and location information.
Trading history and patterns, such as the types of assets traded, frequency, and volume.
Wallet addresses used for deposits and withdrawals, which are used in conjunction with blockchain surveillance software like Chainalysis, using AI to trace your activity under the hood.
Communication records between the user and exchange, including email and chat logs.
Information obtained from third-party sources such as credit bureaus or govt agencies.
What Do VASPs Do with KYC Data?
Once KYC data is voluntarily handed over by a user and collected by a VASP (Virtual Asset Service Provider), the KYC information is typically used for the following purposes:
Compliance: The exchange will use the information to comply with regulatory requirements and anti-money laundering (AML) laws, which require them to verify the identity of their customers and monitor transactions for potential suspicious activity.
Security: KYC information helps VASPS to enhance their security measures and prevent unauthorized access to user accounts and funds, preventing identity fraud and theft.
Customer support: The VASP may use the information to provide customer support, such as verifying account ownership, resolving disputes, or answering questions about the platform and a particular user's order history, interests or activities.
Marketing: In some cases, exchanges may use the information to send promotional materials or offers to users, although this is typically done with the user's consent and can be opted out of.
It's important to be said that the security of your data stored by VASPS is extremely regulated, important and protected, as a customer info leak would be a PR disaster let alone other consequences from regulators, the industry, or their own affected userbase.
However in New Zealand, the IRD (Inland Revenue Department) requests that VASPS hand over KYC information for tax compliance purposes, who are interested in user information such as transaction history, trading volume, wallet addresses, and source of funds.
Disclaimer: All content in this guide is intended for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as financial advice. As an individual, you are entirely responsible for how you conduct your investments and manage your cryptocurrency interests. It is exclusively your own responsibility to perform due diligence and Cryptocurrency NZ recommends taking extreme care and caution with crypto and are not responsible for the outcomes, management, or oversight of your activities.
