Bitcoin & Cryptocurrency Mining Guide NZ – Is it Worth it?
Are you considering taking the leap into crypto mining by setting up your own personal money printing machine in New Zealand? Well if so, you've come to the right place. 😎

To help you on your mining journey, we've created the following guide to lay out the key info on getting started with Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrency mining in NZ.
What is Cryptocurrency Mining in NZ?
Mining is traditionally associated with a pickaxe, but in the realm of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, mining is done by cryptocurrency miners, which are computers.
Crypto mining is the process of solving complex mathematical problems in order to verify transactions on a blockchain network and earn rewards in the form of new crypto coins. It is a way of adding new coins to the network and maintaining its security.
Authors

Contributor

Harry Satoshi
Founder & CEO
Want to know if mining is profitable in NZ?

Cryptocurrency Mining in New Zealand
Cryptocurrency mining is another way to acquire digital assets in New Zealand. Unlike P2P trading, mining involves using computational power to validate transactions and secure blockchain networks, earning rewards in the process.
Yes, you can mine cryptocurrency in New Zealand. In recent years, crypto mining has become increasingly popular in the country, with hundreds of Kiwis and several companies actively participating in the NZ crypto mining industry.
New Zealand offers several advantages for cryptocurrency mining, including access to renewable energy, a stable political environment, and a growing technology sector. The country's abundant natural resources, including wind and hydro power, provide an attractive environment for energy-intensive mining operations.
Is Mining Profitable in NZ?
Bitcoin and cryptocurrency mining in NZ can be profitable under the right circumstances, but success depends on several critical factors. The cost of electricity is paramount, with prices exceeding 20 cents per kilowatt-hour (NZD) making it less lucrative. Additionally, the price of cryptocurrencies, mining hardware efficiency, and mining difficulty all factor into profitability.
Mining Options in NZ
Solo Mining
Solo mining involves mining cryptocurrency independently, without joining a pool. The miner assumes full control over the operation and receives the full reward for any blocks mined, but chances of success are lower due to competing with large mining operations.
Pool Mining
Pool mining involves multiple miners combining their computational resources to mine cryptocurrencies collectively. Miners join a group working toward earning rewards together, increasing the chances of regular payouts but receiving a proportional share based on contributed hash power.
Warning: Cryptocurrency NZ does NOT recommend cloud mining services. This sector is known for scams and fraudulent operations. Always do thorough research before investing in any mining operation.
Trusted Hosting Services
If you don't want to manage mining hardware yourself, CryptoMate is the largest mining hosting company in New Zealand. They offer Kiwis a service for hosting ASIC and GPU mining equipment, delivering an efficient experience tailored to customer needs and requirements.
Disclaimer: All content is intended for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as financial advice. You are entirely responsible for your investment decisions. Cryptocurrency NZ recommends taking extreme care with crypto investments and is not responsible for the outcomes of your activities.
Bitcoin Mining in NZ
What is Bitcoin Mining in NZ?
Bitcoin mining is the process of verifying and adding transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain. Miners use specialized hardware to solve complex mathematical problems and compete with other miners to add a block of transactions to the blockchain.
Is Bitcoin Mining Profitable in NZ?
Whether Bitcoin mining is profitable in New Zealand depends on several factors such as the cost of electricity, price of Bitcoin, and efficiency of the mining hardware being used. The cost of electricity in NZ ranges from 0.19-0.25c NZ making it somewhat profitable.
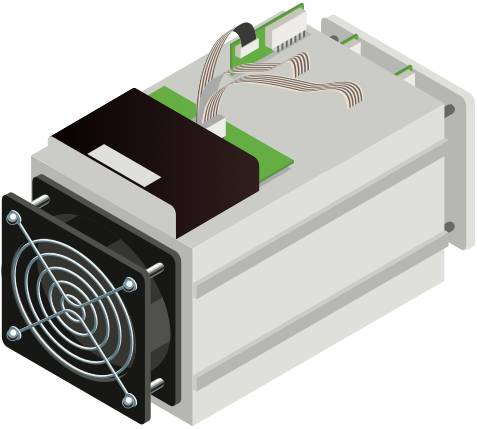
ASIC Mining in New Zealand
ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit) mining is a type of cryptocurrency mining that uses specialized hardware designed specifically for mining. Unlike GPU mining, which uses general-purpose graphics cards, ASICs are designed to perform one specific task extremely efficiently.
ASIC Mining Considerations
- Supported cryptocurrencies: ASIC miners are designed for specific coins like Bitcoin and Litecoin
- Rig location: Requires well-ventilated space due to heat and noise generation
- Power consumption: Substantial power requirements may need electrical system upgrades
Essential Mining Tools
- Whattomine: Provides calculations on the most profitable coins to mine
- Minerstat: Offers tools and services for crypto miners, including monitoring
- ASIC Miner Value: Provides data on market value and specifications of ASIC machines

To help you on your mining journey, we've created the following guide to lay out the key info on getting started with Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrency mining in NZ.
What is Cryptocurrency Mining in NZ?
Mining is traditionally associated with a pickaxe, but in the realm of Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, mining is done by cryptocurrency miners, which are computers.
Crypto mining is the process of solving complex mathematical problems in order to verify transactions on a blockchain network and earn rewards in the form of new crypto coins. It is a way of adding new coins to the network and maintaining its security.
Mining Hardware Options
When getting started with cryptocurrency mining in New Zealand, you have several hardware options to consider. The most common types include ASIC miners, GPU mining rigs, and CPU mining.
GPU Mining in New Zealand
GPU mining is the process of using a graphics processing unit (GPU) to mine crypto by solving complex mathematical problems and validating transactions on the blockchain. This method of mining is used as an alternative to using specialized mining hardware, such as ASICs, and it can be more flexible and cost-effective in New Zealand.
However, it can also be more energy-intensive and less profitable compared to other forms of mining, so it is important to carefully consider the costs and potential rewards.
Is GPU Mining Profitable in NZ?
Profitability depends on factors including the current difficulty level of the cryptocurrency you want to mine, the price of that cryptocurrency, the cost of electricity, and the cost of the hardware. In general, the profitability of GPU mining is impacted by the overall crypto market which can be volatile. TLDR: With Ethereum out of the picture GPU profitability has plunged.
Cryptocurrency NZ recommends using online mining calculators to estimate the potential rewards and determine whether GPU mining is currently profitable in New Zealand. Whattomine and Minerstat are two great tools to have in the back pocket.
Hardware Required for GPU Mining in NZ
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The most important component of a mining rig is the GPU. Choose a GPU with a high hash rate and power efficiency for the cryptocurrency you want to mine.
- Motherboard: A motherboard that is compatible with your chosen GPU and has multiple PCI-E slots for multiple GPUs.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): A high-quality and efficient PSU is necessary to power the GPUs and other components of the rig. Make sure it can deliver enough power for your setup.
- Memory (RAM): A minimum of 8GB of RAM is recommended for GPU mining.
- Storage: A solid-state drive (SSD) is recommended for the operating system and mining software, while a larger hard drive can be used for data storage.
- CPU: A basic CPU is sufficient for GPU mining, as the GPUs will do most of the heavy lifting.
- Mining Rig Frame: A sturdy frame is necessary to securely house and cool the components of the rig.
- Fans: High-quality cooling fans are essential to keep the GPUs and other components cool and operating efficiently.
- Riser Cables: Riser cables are used to connect the GPUs to the motherboard and provide additional space between them.
Kiwi Crypto Miner - Our Local Cryptocurrency Mining Expert
Want to learn more about GPU Mining? We have our local expert Kiwi Crypto Miner who specializes in AMD and Nvidia cards and obtaining maximum efficiency. Can also find his GPU Comparison sheet here.
Go to Kiwi Crypto Miner's YoutubeCPU Mining in New Zealand
CPU mining, also known as Central Processing Unit mining, is the process of using the computational power of a computer's CPU to perform cryptocurrency mining. It involves utilizing the processing capabilities of a computer's CPU to solve complex mathematical problems, which are necessary for confirming and validating transactions on a blockchain network.
A notable example of a CPU mineable token is Monero (XMR), which utilizes the CryptoNight algorithm.

Is CPU Mining Profitable in NZ?
While it is technically possible to mine crypto using a central processor (CPU), it is no longer efficient or profitable in 2025.
Crypto mining demands substantial computational power, which CPUs are not equipped to deliver at competitive levels. Specialized mining hardware, such as ASICs and GPUs, have been purpose-built for mining and offer higher computing power.
CPU Mining NZ Essential Tools
- XMRig: An open-source software specifically developed for crypto mining, including popular cryptocurrencies such as Monero and Bitcoin.
- NiceHash: A website that offers a marketplace and platform for buying and selling hashing power, allowing users to rent or lease their mining capabilities.
- Minerstat: A website that offers a large suite of tools and services for crypto miners, including monitoring and management.
What Is the Difference Between CPU Mining and GPU Mining?
CPU mining and GPU mining are two hardware-based methods used for cryptocurrency mining in New Zealand.
CPU mining involves utilizing a computer's central processor to carry out intricate mathematical computations necessary for validating transactions on a blockchain and producing new coins. On the other hand, GPU mining employs a specialized graphics processing unit capable of performing numerous calculations concurrently, making it more efficient compared to CPU mining.
As a consequence, GPU mining is generally more profitable for mining most cryptocurrencies. However, there might still be certain cryptocurrencies that have lower computational requirements, allowing for profitable CPU mining in New Zealand.

Essential Tools For Cryptocurrency Mining in NZ
- Whattomine: A website that provides cryptocurrency miners with information and calculations on the most profitable coins to mine based on various factors.
- Minerstat: A website that offers a large suite of tools and services for crypto miners, including monitoring and management.
- ASIC Miner Value: A website that provides information and data on the current market value, profitability, and specifications of various ASIC mining machines.
- NiceHash: A website that offers a marketplace and platform for buying and selling hashing power, allowing users to rent or lease their mining capabilities.
- CryptoMate Dunedin: A Dunedin based Hosting Facility. They make mining crypto cost-effective, simple and accessible for everyone.
- Mining Pool Stats: A website that provides real-time information and statistics on various mining pools.
- Hiveon: A website that provides a comprehensive mining platform and tools for crypto miners, including mining pool services, monitoring and statistics.
- BTC.com: A website that offers data about Bitcoin and other POW tokens difficulty, Pool Distribution and more.
Want to know if mining is profitable in NZ?
Cryptocurrency Mining Tax in NZ

In New Zealand, tax laws surrounding crypto mining can be complex and confusing. It is important to understand it thoroughly.
The New Zealand Inland Revenue Department (IRD) has issued guidance on the tax treatment of cryptocurrency, including mining. The IRD considers income from cryptocurrency mining as taxable income, subject to income tax. This means that any profits made from cryptocurrency mining in New Zealand must be reported in your annual income tax return.
Seeking professional advice from a tax expert will help you to navigate the complexities of New Zealand tax laws.
Cryptocurrency NZ Final Verdict
Mining crypto in NZ presents both opportunities and challenges. While the country offers advantages like reasonable electricity costs, a robust internet infrastructure, and government support, it's important to acknowledge the difficulties that come with it.
Fluctuating cryptocurrency prices, evolving tax regulations, and changing regulations can make mining operations more complex. Therefore, Kiwi miners should conduct thorough research, stay informed, and leverage available resources such as mining calculators, online communities, and hardware retailers to maximize profitability and stay up-to-date with developments.
While it may not be without obstacles Cryptocurrency NZ believes with the right tools, knowledge, and support, cryptocurrency mining in New Zealand remains a dynamic opportunity for those willing to explore this exciting frontier.
Commonly Asked Questions
Why do Bitcoins need to be mined?
Bitcoins need to be mined for several reasons:
- Security and Verification: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network called a blockchain. Mining plays a vital role in securing the network by verifying and validating transactions. Miners use their computational power to solve complex mathematical problems, which helps confirm the authenticity of transactions and prevents double-spending.
- Creation of New Bitcoins: Through the mining process, new bitcoins are introduced into circulation. Miners who successfully validate transactions and solve the mathematical puzzles are rewarded with newly minted bitcoins. This process, known as the block reward, incentivizes miners to contribute their computational power and support the network's operations.
- Transaction Processing: Miners include pending transactions into blocks and add them to the blockchain. They prioritize transactions based on various factors such as transaction fees, ensuring the smooth processing of Bitcoin transactions across the network. Miners play a crucial role in maintaining the overall functionality and efficiency of the Bitcoin network.
How does mining confirm transactions?
Mining confirms transactions by including them in blocks. Miners collect pending transactions from the network's mempool and group them into blocks. They then compete to solve a mathematical puzzle, known as Proof-of-Work, by performing intensive computational calculations.
Does mining use a lot electricity?
Yes, mining does consume a significant amount of electricity. The process of mining involves the use of powerful hardware, such as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) or GPUs, which require a substantial amount of electrical power to perform the necessary computational calculations.
Does crypto mining damage your GPU/computer?
Mining can put strain on GPUs and computers due to the high workload and heat generation. If proper cooling measures are not in place, it can potentially lead to overheating and damage to the hardware. Using appropriate cooling solutions and monitoring temperatures can help mitigate these risks.
Disclaimer: All content in this guide is intended for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as financial advice. As an individual, you are entirely responsible for how you conduct your investments and manage your cryptocurrency interests. It is exclusively your own responsibility to perform due diligence and Cryptocurrency NZ recommends taking extreme care and caution with crypto and are not responsible for the outcomes, management, or oversight of your activities.